You are receiving this email from a list acquired in the Orange County Business Journal. |
| |
|
August 17, 2011 |
|
| SQL Database Best Practices! |
SQL MAINTENANCE PROGRAM:
Having a good solid maintenance strategy as part of your SQL Server database is a necessity for any company with a business critical
application. It can be the difference of being down for a few minutes vs. being down for an entire day or several days. It can also manage
space on the server better and if done correctly, can improve performance of the database dramatically.
The first part of a good database management strategy is to plan your backups. For a database that is frequently used and important to the
company we recommend the following standard maintenance plan. In general it's a good idea to do a full backup twice a day and
transaction log backups hourly so you can easily restore the database up to the hour within minutes.
1. Back Up Full Databases Twice Daily
There are three Recovery Models
a. Full Recovery Model - What Roundbrix mostly uses. Safest mode of operation for production systems.
b. Bulk-Logged Recovery Model - Has minimum logging for bulk import operations. Space allocation and deallocation is only
logged for bulk import operations. Basically a few limitations.
c. Simple Recovery Model - No transaction log maintenance needed. Recoverability of the database is very limited to a
specific time frame.
If a database doesn't change often, Simple Recovery Model may be an option. (i.e. a database that imports all the data from Quickbooks
from previous day, etc.). The data is only used for reporting, so the Simple Recovery Model would work fine if timed properly. (after data
is inputted from QB).
2. Back Up Transaction Log Files Hourly
A database has two components, data file(s) and transaction logs. A transaction log captures the modifications made to the database. A
SQL server must have at least one transaction file.
With the Full Recovery Model, it is important to backup the transaction logs frequently so the database can be restored up to the point in
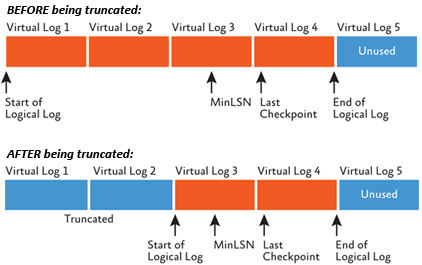
time when the problem occurred. A transaction log backup will truncate the inactive portion of the transaction log.
The transaction log can get large and the file size will not be reduced when it is truncated after a transaction log backup. This simply shifts
the pointer within the existing file as to where the space is to be freed up.
3. Rebuild Indexes Weekly
Rebuilding indexes should be done weekly during off-hours as this can sometimes be intensive and slow down the database. It is important
to rebuild the indexes to optimize performance of the database. You can think of this like defragmenting your hard drive. After it is
completed, everything runs just a little smoother and faster because space is optimized properly (doesn't take as long to figure out where a
record goes during an insert or update).
4. Update Statistics Daily
It is also a good idea to create a maintenance plan to update statistics daily. This optimizes space in the tables and can have an impact on
improving performance of the database. If this never gets done (which sometimes happens in databases that are not maintained)
performance can slowly degrade until it becomes a serious problem, adversely affecting application performance.
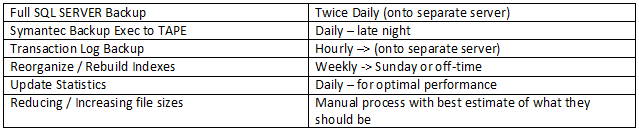
TYPICAL BACKUP PLAN FOR A DATABASE THAT IS BUSINESS-CRITICAL:
PROPER AND OPTIMAL DATABASE DESIGN:
One of the most common problems we've seen is applications where a query takes over 30 seconds only to find that one of the fields in that
query has not been indexed. Beyond looking at the queries in your application to make sure the fields that are in your "WHERE" clauses are
all indexed, there are some tools that can help. Using Microsoft SQL Server Profiler in combination with Database Engine Tuning Advisor is
the easiest way to find slow queries and see what indexes may be missing, which could help improve the performance of your application.
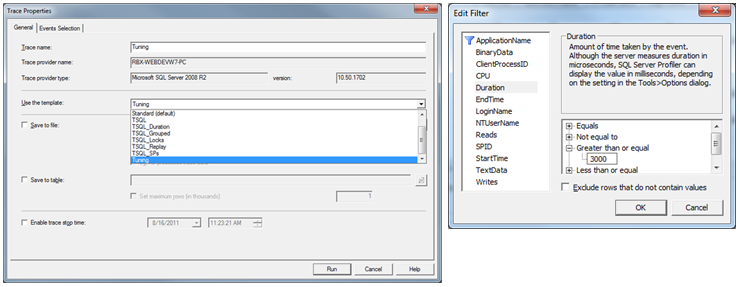
For SQL Server Profiler first, select "Tuning". Next, select the "Events Selection" tab, and then the "Column Filters..." option and "Duration".
Select the Greater than or equal to 3000, as we want to see queries taking over 3 seconds.
After about an hour of running the profiler, stop it. You should save the file to one that can be imported into a "Database Engine Tuning
Advisor". Run it to have the tool point out what can be optimized. Usually you can accept most of the suggestions from Database Engine
Tuning Advisor and see a dramatic increase in performance.
The other important thing to look at in a database is how well normalized it is. Normalization is important so that information is not
duplicated. One example is a company we worked with used 12 different excel sheets to keep track of similar information. However data that was supposed to be consistent throughout the different excel files was spelled differently and listed multiple times where it should have referenced by a table with a unique ID and one consistent value.
We moved these 12 excel sheets into one database and created separate tables for the columns so information was normalized. This
allowed the customer to do more sophisticated and accurate queries on their data.
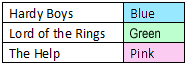
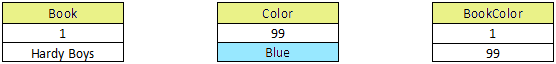
The information above, when properly normalized, should be put into three tables as shown below. This way, "Hardy Boys" only needs to be updated once.
PROPER NAMING CONVENTION IS ALSO IMPORTANT:
Naming a foreign key differently from the primary key that it references can be very confusing to programmers. If the fields are named
properly and referenced properly, it can save countless hours of confusion. I typically name the primary key as the table name with "ID"
after it. So if Book is the table, BookID is the primary key. This is a pretty common way to name primary keys which will make it easier for
programmers to understand more quickly.
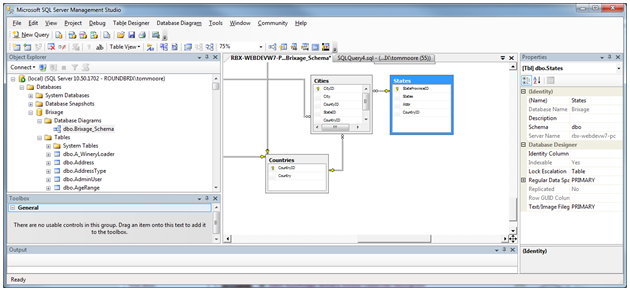
It is also important to make sure you keep an ER (Entity-Relationship) Diagram. This is very easy with SQL Server by right clicking on Database
Diagrams and selecting "New Database Diagram". Then you can link the primary/foreign keys here and also add/update fields to the
database-making database management tool very easily. Make sure all the tables are in the diagram and connected properly to the other
tables that they should be connected to.
By following the tips above, you should have a solid robust database that will allow your company to grow without having to worry about
database issues. For a free database analysis call the experts at roundbrix at 949.273.5200.
|
|

|
23172 Plaza Pointe, Suite 285, Laguna Hills, CA 92653 |
To make sure this and future emails arrive in your inbox rather than your junk mail folder, add "noreply@roundbrix.com" to your
address book or safe list. To unsubscribe from this type of email,click here. Having trouble viewing this email?Click here. | |







